IKB Smart District
Name and address
IKB Smart District
Langer Weg 32
6020 Innsbruck
Map
Source: Google Maps

Type of installation
The IKB-Smart-District includes several buildings. In the center is the Showroom were most of the units are located. On nearly all roofs PV plants are installed. Between the location “heating room” and the Showroom the heat pipes were built, and a micro heating grid installed. The heat storage tanks are located in the Showroom and the heating room. The other departments like the Recycling Center and the electricity grid department are connected by a micro gird for electricity. Charging stations for the electrical cars are also located close by the showroom.
Ownership
Innsbrucker Kommunalbetriebe AG
Capacity
Biogas CHP
262 kWel / 375 kWth
Heat Pumps
2 x 95.7 kWth
Heat storage Tanks
1 x 10,000 litre
6 x 1,500 litre
Electric heating element
200 kWel
Heat exchanger sewage water
150 kWth
PV-plant – LW32
14.82 kWp
PV-plant – RCH
122.58 kWp
PV-plant – Triendlgasse
50.76 kWp
Battery storage
27.60 kWh
Detailed characteristics of the device / infrastructure / service
The project “IKB Smart District” includes the following major components:
- Biogas CHP
- Heat Pumps
- Heat storage Tanks
- Electric heating element
- Heat exchanger sewage water
- PV-plants
- Sensors- & monitoring equipment
- Battery storage
Concept
The figure below shows a simplified schematic representation of the project:
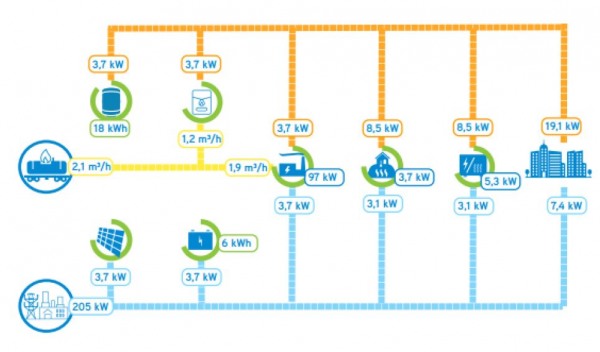
Energy solutions
The aim of the project was the implementation of an innovative hybrid grid to connect the different sectors of electricity, heat and gas. For this purpose, several technical facilities, such as: heat pumps, CHP, heat storage tanks, battery storages, PV systems and a sewage water heat exchanger were built.
Technologies considered in the design
Biogas-CHP:
As part of IKB Smart District project, a new biogas CHP were installed within showroom to convert biogas (biogas use proven through certificates) into electricity and heat. The electric power is 262 kW and the thermal power 375 kW.
Heat pumps:
Heat pumps are considered a key technology to integrate the heating sector into the electricity-based energy system. These devices use electricity to circulate hot/cold liquids, using the heat from outside air, geothermal heat, ground or sewage water. As part of IKB Smart District project, two heat pumps with a thermal power of 95.7 kW for each were installed. As an energy source, the wastewater from the nearby sewer is used.
Heat storage tanks:
To store the generated heat, several heat storage tanks with a total capacity of 19 m³ were built. The large storage tank with 10 m³ is situated in the showroom of Langer Weg 32 and the storage cascade with 9 m³ (6 x 1.5 m³) were situated in the technical room of Rossaugasse 2.
Electric heating element:
The installed Power-to-heat system is operated according to the flow heater principle and has an electrical power of 200 kW. Due to the almost lossless conversion, the thermal performance of 200 kW is also obtained. All components of the power-to-heat system (continuous flow heater, heat exchangers, main pumps, control technology) are located in the showroom of the project.
Inline heat exchanger for sewage water:
The installed inline heat exchanger is a module sewer heat exchange system for subsequent installation in existing sewers. The modules are introduced into the sewer using the available shaft infrastructure and are securely mounted. The heat exchange surface is completely supplied by warm wastewater (between 8°C and 22°C). The heat exchanger itself is perfused with heating water. Energy is thus extracted from the warm wastewater.
PV systems:
In addition to the existing PV plants, several new PV plants with a total capacity of 188.16 kWp were built. The new plants were integrated into the overall system.
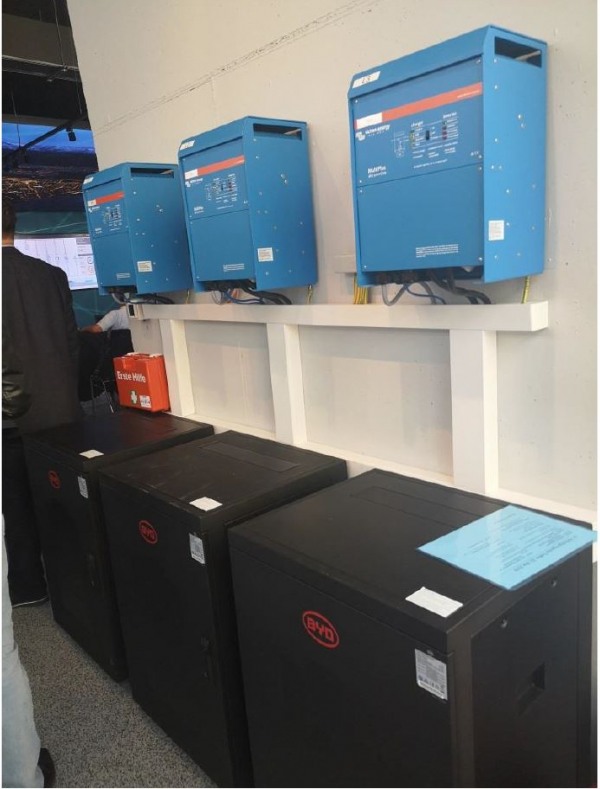
Battery storage:
To match electricity supply and demand a battery storage with a capacity of 27.60 kWh has been installed in the showroom. As technology, a lithium-iron-phosphate battery was used.
Performance targets
expected amount of produced heat: 1,855 MWh/a
expected amount of produced electricity: 1,020 MWh/a
expected amount of reduced CO2: 863 t/a
Financing model
Direct investment of IKB 85%, national grant: 10 % and EC grant: 5%
Contracting authority: IKB Innsbrucker Kommunalbetriebe AG
Project manager: Sophia Neuner (IKB)
Manufacturer / supplier: Ortner (pipeline construction and main components); Doma (measuring and control technology); Uhrig (sewage water heat exchanger)
Cost breakdown
The total investment costs are in order of 3.2 Mio. €, Estimated payback time is: 10a
Implementation planning
1 - Design: 05/2017
2 – Public procurement: 01/2018
3 – Completion: 04/2019
Work progress
Milestones
Figure 1: CHP plant in the IKB Smart District fired with biogas
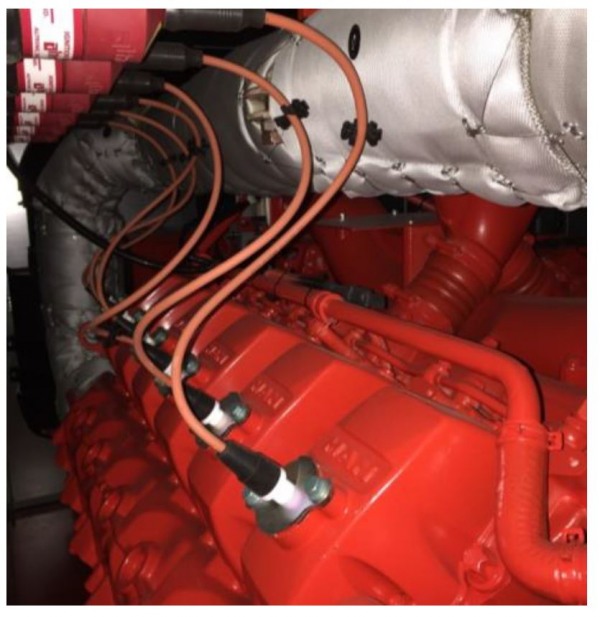

Figure 2: One of two heatpumps in the IKB Smart District
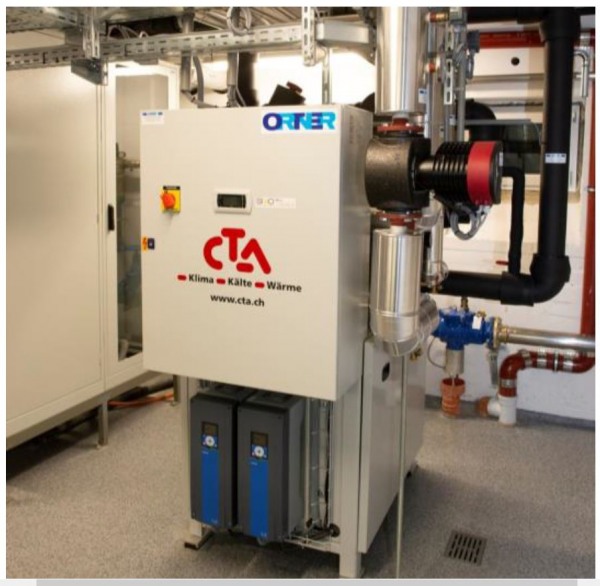

Figure 3: Heat storage tank cascade – 6 x 1,500 litres
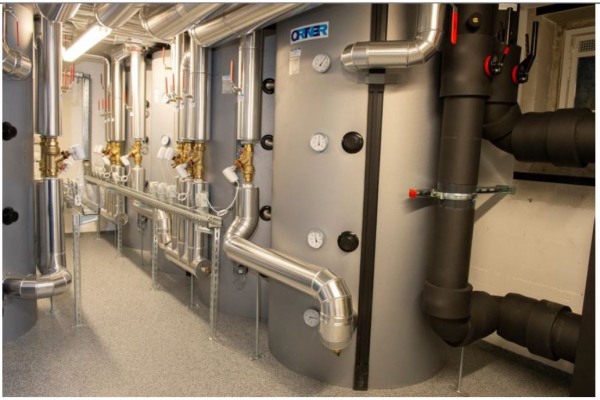

Figure 4: Power-to-heat system in the IKB-Smart-District
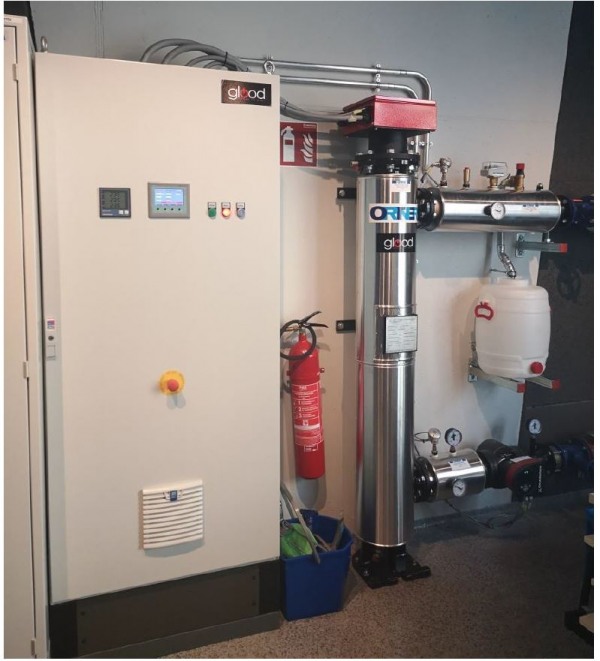

Figure 5: Inline heat exchanger for sewage water
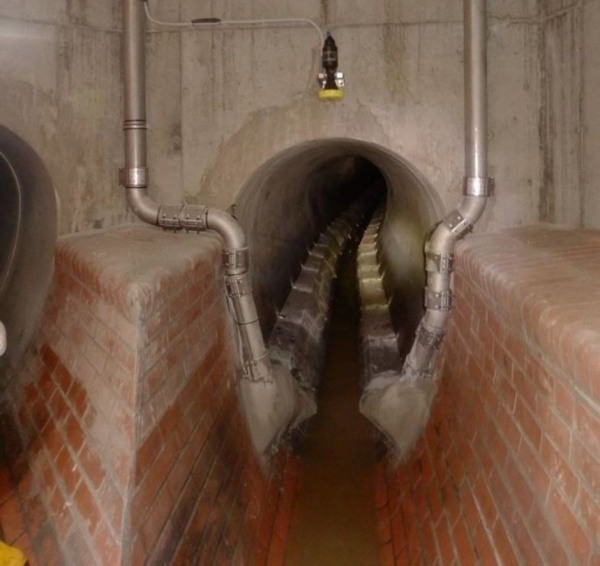

Figure 6: PV plant Showroom - Langer Weg 32
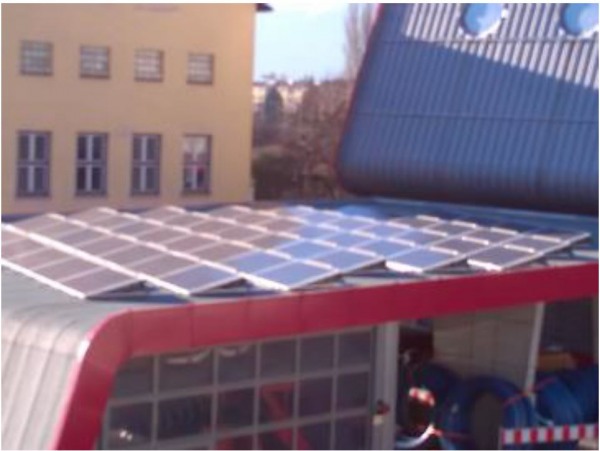

Figure 7: PV plant -Recycling Center - Rossaugasse 4
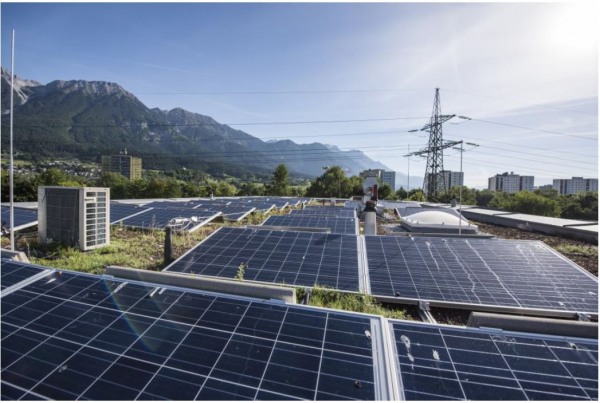

Figure 8: PV plant - Trientlgasse
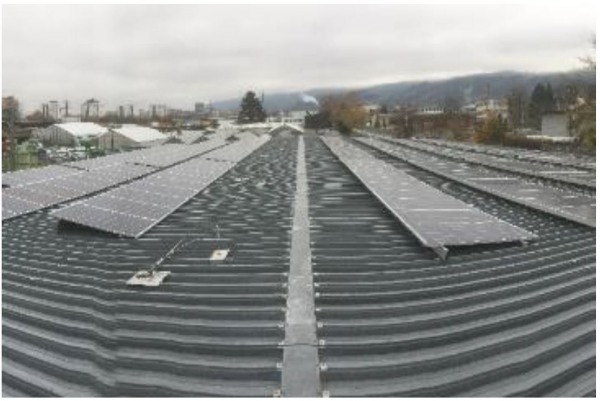

Figure 9: Battery storage – Langer Weg 32

Monitoring System
The entire system has a modern process control system, which connects all components with each other. All measured values required for operation are recorded in the system. In order to assess the performance of the individual components, KPIs are calculated.
Monitored variables and figures
The following data is recorded for the Sinfonia project:
- energy input and output [kWhel, kWhth]
- reduction of CO2 [t/a]
Heat pumps: 20 yrs
Biogas CHP: 20 yrs
Measuring and control system: 15 yrs
Sewage water heat exchanger: 20 yrs
PV plants: 20 yrs
Buildings: 50 yrs
Pipe systems: 20 yrs
Battery storage: 8 yrs
Heat storage tanks: 20 yrs

Building owner
IKB Innsbrucker Kommunalbetriebe AG
Manufacturer/Supplier
Ortner (pipeline construction and main components)
Doma (measuring and control technology)
Uhrig (sewage water heat exchanger)
Contact
Sophia Neuner (IKB)
Project Manager







